The Honours Project was done under the joint supervision of Arash Bakhtiari (TUM), Dirk Hartmann and Utz Wever (Siemens)
Topology optimization is becoming an increasingly important tool in CAD. Several open-source topology optimization tools already exist, but are generally unsuitable for efficient incorporation in a design process, as there is no straightforward way to reacquire an editable CAD format. For this purpose, the software CADO (Computer Aided Design Optimizer) was developed. The software incorporates a topology optimiser, which works on voxelized CAD designs, and gives back outputs in voxel grid representations. An algorithm to retrieve a CAD-ready surface representation of this data was designed. From the voxel data, a surface is extracted using Dual Contouring. This is reconstructed into a network of tensor product NURBS surface patches using a linear least-squares fitting scheme. The constraint to get smooth connections between the patches is applied by fitting to another network of points, related to the surface through a slightly modified version of the scheme of Peters. The NURBS surface patches are then readily converted to a standard CAD format, and other constraints are taken into account.
This project was conducted in cooperation with Siemens and had as a goal to deliver a software which is able to iterate through the whole pipeline from a CAD model over topology optimization back to CAD.
Motivation
A common problem in product design is to create a functioning structure using as little material as possible. Three decades ago, engineering design versions were drawn, prototypes created and experimental test performed. Nowadays, the field of topology optimization simplifies this process and stands as a powerful tool in engineering and design.
Topology optimization tackles the problem of material distribution in a structure in order to fulfil certain target loads. Several topology optimization open-source tools exist that are ready to use; however, it is still a challenge to incorporate these tools smoothly in the design process. The idea of this project is to allow these tools to work starting directly from CAD files and to transfer the resulting mesh-based solution back to the CAD world. Unfortunately, at the moment, there is no open-source solution for the conversion of mesh-based geometry to the spline-based CAD format. The common approach of converting each triangle of a mesh geometry directly into CAD format results in enormous file sizes. One of the biggest challenges of this project is thus to develop a conversion tool that feasibly provides a useful CAD-representation of the optimized surface.
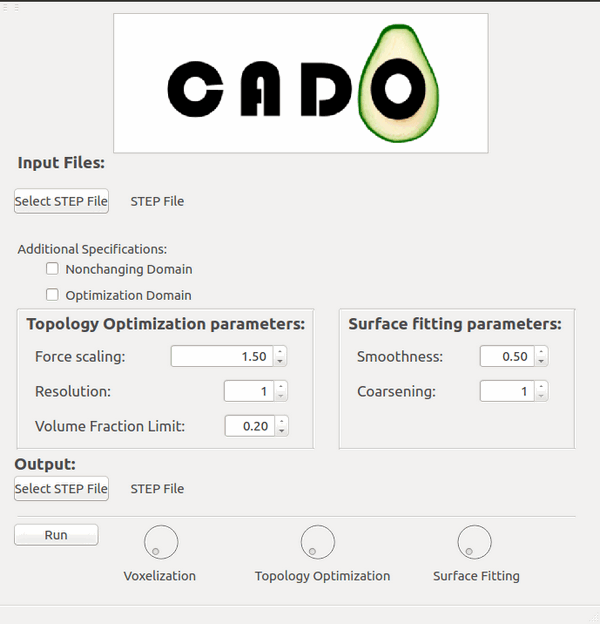
Figure 1: CADO offers all the functionalities needed to optimize a given topology.
Development overview
CADO works as a fully integrated tool-chain from the CAD input file to an optimized CAD file. First, the input geometry undergoes voxelization using OpenCASCADE to ensure compatibility with the topology optimizer. Second, the topology is optimized by employing the open-source tool ToPy. Next, a two-stage Dual Contouring surface reconstruction scheme is executed on the output of topology optimization. This gives us coarse parametrization patches and fine vertices as output. A B-Spline surface is then fitted through this data by a least-square approach using control points described by the Peters’ scheme. In order to ensure continuous and smooth surfaces. Lastly, a FreeCAD macro script performs boolean operations to enforce geometric constraints and exports the geometry to a standardized CAD file.
In summary, the process can be subdivided into six steps:
- CAD model:
Initial design of the part including boundary conditions and applied forces. - Voxelization:
Most topology optimizers need a voxel grid to work with. Since CAD formats are based on surfaces we first use an OpenCascade voxelizer to create a corresponding voxel grid. - Topology Optimization:
The topology optimizer of choice was ToPy- an opensource tool written by William Hunter. - Surface Extraction:
Dual contouring is used to extract a surface from the optimized voxel model. - Surface Fitting:
Peters’ Scheme is applied for fitting a surface of G1 continuously connected B-Spline patches to the extracted surface points. - Boolean Operation:
By applying a boolean operation at the end to the optimized structure, we are able to define non-changing or cut-off regions.
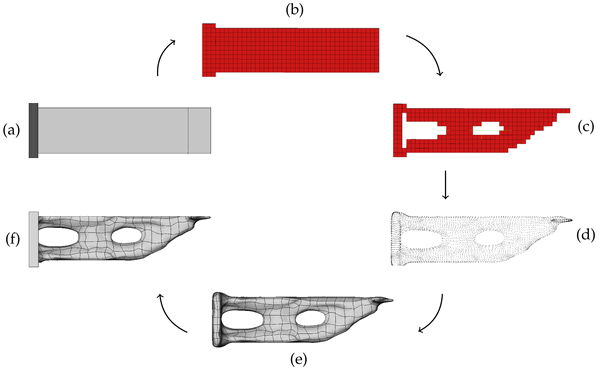
Figure 2: Pipeline of CADO
Features of the final software
- Full topology optimization design cycle
- User interaction only in the CAD world
- Output as standard .step files with NURBS geometry
- Modular design for exchangability of components
- Extensive code documentation
- Completely Opensource under BSD license (CADO on Git)
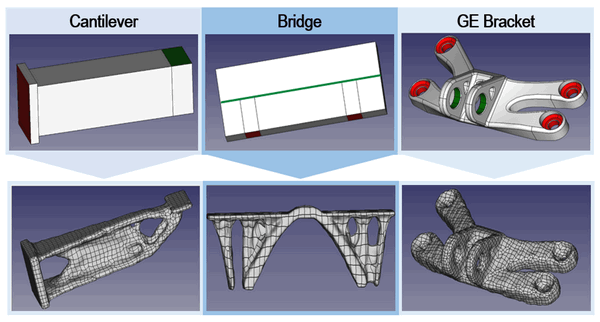
Figure 3: CADO applied on three test cases Cantilever, Bridge and GE Bracket.
